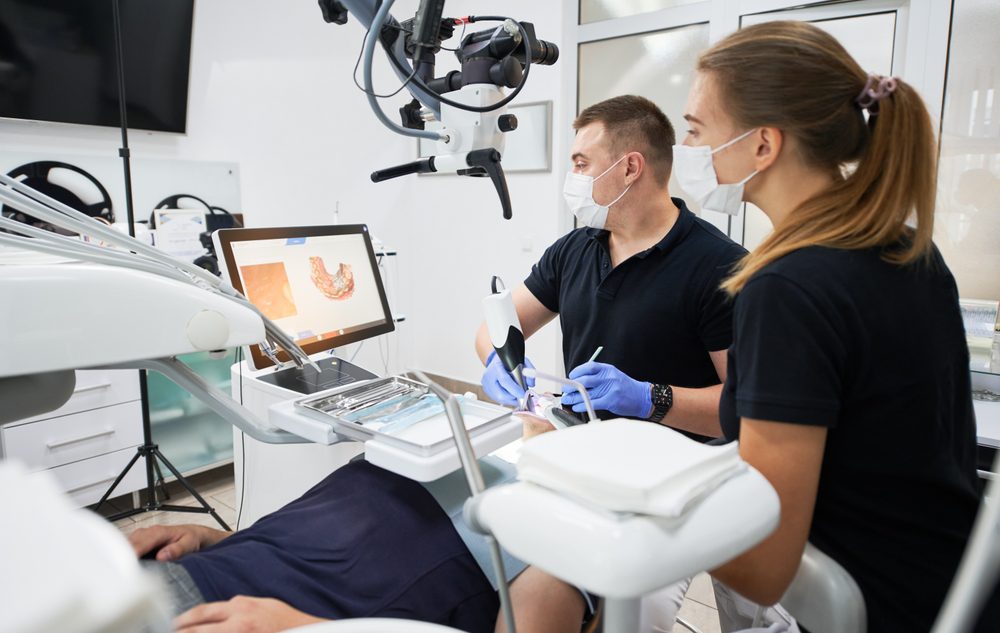
An intraoral sensor is a pivotal component in modern dental diagnostics, marking a significant leap from traditional dental X-ray film. This compact, technologically advanced device is designed to capture high-resolution images of a patient’s teeth and the surrounding oral structures, playing a crucial role in dental examinations and treatments.
The Basics of Intraoral Sensors
Intraoral sensors belong to the category of digital radiography. They are used in place of traditional photographic X-ray film and are inserted into a patient’s mouth to capture dental images. These sensors are connected to a computer and, when exposed to X-rays, they capture the image and immediately transfer it to the computer screen.
Technology Behind the Intraoral Sensor
These sensors operate on the principle of direct digital radiography (DDR). They contain an array of photodetectors, typically made of a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS). These photodetectors convert X-ray photons into electrical signals, which are then digitized and displayed as images.
Sizes and Ergonomics
Intraoral sensors come in various sizes to accommodate different patients, including children. Ergonomically designed, they are often encapsulated in a waterproof casing for hygiene and durability. Some are equipped with rounded edges and thin profiles to enhance patient comfort.
Image Quality and Efficiency
The image quality provided by intraoral sensors is a significant upgrade over traditional film. They offer higher resolution images with greater detail, aiding in more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. The efficiency of image processing with intraoral sensors is remarkable – images appear on the screen within seconds of exposure, speeding up the examination process.
Radiation Exposure
One of the notable benefits of intraoral sensors is the reduced radiation exposure required to obtain images. They are more sensitive to X-rays than traditional film, meaning that lower doses can be used to achieve the same or better quality images, enhancing patient safety.
Integration with Dental Practice Management Software
Intraoral sensors seamlessly integrate with dental practice management software, facilitating easy storage, retrieval, and management of patient images. This integration enhances record-keeping efficiency and aids in treatment planning and tracking progress over time.
Environmental Impact
Unlike traditional X-ray films that require chemical processing, intraoral sensors are environmentally friendly. They eliminate the need for film and development chemicals, thus reducing waste and chemical exposure in the dental office.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in intraoral sensors may be higher than traditional X-ray systems, they are cost-effective in the long run. They eliminate ongoing expenses related to film, developing chemicals, and storage. Their durability also means that they need not be replaced frequently.
Applications in Dentistry
Intraoral sensors are used across various dental specializations. In restorative dentistry, they assist in identifying caries and assessing restorations like fillings and crowns. In endodontics, they are crucial for visualizing root canals, while in periodontics, they help assess bone levels. Orthodontists use them to monitor tooth movement and alignment.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, intraoral sensors have some limitations. Their size can sometimes be uncomfortable for patients, especially when capturing images of the back teeth. Also, the sensor must be repositioned multiple times to capture different areas, which can extend the duration of the procedure.
Future Advancements
The field of intraoral sensors is continually evolving. Future advancements may focus on enhancing image quality further, reducing sensor size for patient comfort, and improving integration capabilities with other digital dental tools.
Training and Adaptation
Successful implementation of intraoral sensors requires training for dental professionals. This training ensures that practitioners can effectively and safely use the sensors and interpret the images they produce.
Patient Education and Acceptance
Educating patients about the benefits of digital imaging with intraoral sensors, such as reduced radiation exposure and quicker appointment times, can enhance patient acceptance and comfort.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Dental practices must adhere to legal standards for storing and protecting digital radiographs. Ensuring data security and patient confidentiality is paramount in the digital age.
In conclusion, the intraoral sensor represents a significant advancement in dental radiography, offering numerous benefits over traditional X-ray film. Their ability to provide high-resolution images rapidly, with reduced radiation exposure, makes them an invaluable tool in modern dental diagnostics and treatment. As technology continues to advance, we can expect these sensors to become even more integrated into dental practices, further enhancing patient care and treatment outcomes. Contact Great Lakes Imaging today to learn more!
